When you get hungry, you grab a snack from your fridge or pantry. But what can plants do when they get hungry? You are probably aware that plants need sunlight, water, and a home (like soil) to grow, but where do they get their food? They make it themselves!
Plants are called autotrophs because they can use energy from light to synthesize, or make, their own food source. Many people believe they are “feeding” a plant when they put it in soil, water it, or place it outside in the Sun, but none of these things are considered food. Rather, plants use sunlight, water, and the gases in the air to make glucose, which is a form of sugar that plants need to survive. This process is called photosynthesis and is performed by all plants, algae, and even some microorganisms. To perform photosynthesis, plants need three things: carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight.
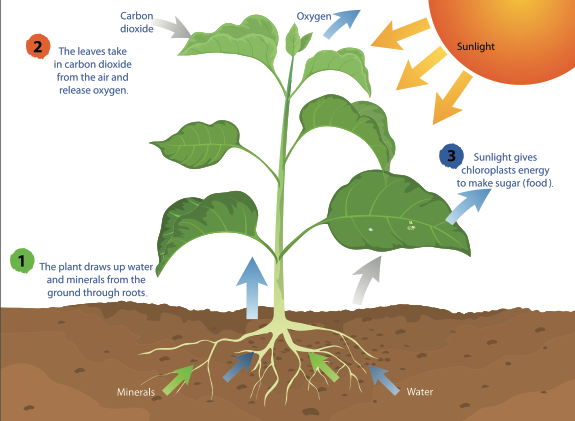 By taking in water (H2O) through the roots, carbon dioxide (CO2) from the air, and light energy from the Sun, plants can perform photosynthesis to make glucose (sugars) and oxygen (O2). CREDIT: mapichai/Shutterstock.com
By taking in water (H2O) through the roots, carbon dioxide (CO2) from the air, and light energy from the Sun, plants can perform photosynthesis to make glucose (sugars) and oxygen (O2). CREDIT: mapichai/Shutterstock.com



 By taking in water (H2O) through the roots, carbon dioxide (CO2) from the air, and light energy from the Sun, plants can perform photosynthesis to make glucose (sugars) and oxygen (O2).
By taking in water (H2O) through the roots, carbon dioxide (CO2) from the air, and light energy from the Sun, plants can perform photosynthesis to make glucose (sugars) and oxygen (O2). 






